The Evolution of AI—From Simple Algorithms to Thinking Machines
The story of artificial intelligence (AI) is a tale of human ingenuity, ambition, and relentless innovation. While the concept of machines mimicking human intelligence dates back to ancient civilizations—think of Greek myths about automatons or medieval tales of mechanical knights—the modern journey of AI began in the 20th century.
The Birth of AI (1950s–1980s)
In 1950, Alan Turing posed a revolutionary question: “Can machines think?” His seminal paper, “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” introduced the Turing Test, a benchmark for machine intelligence. Six years later, the Dartmouth Conference formally coined the term “Artificial Intelligence” and set the stage for decades of research. Early AI systems, like the Logic Theorist (1956) and ELIZA (1966), relied on rule-based programming—hard-coded instructions to solve specific problems. These systems were groundbreaking but rigid, limited to narrow tasks like solving math theorems or simulating simple conversations.
The Rise of Machine Learning (1990s–2010s)
The limitations of rule-based AI became apparent as the world grew more complex. Machine learning (ML)—a paradigm shift where algorithms learn from data instead of following explicit rules. ML-powered systems, like IBM’s Deep Blue (which defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997) and early recommendation engines, demonstrated AI’s potential to adapt. By the 2010s, deep learning—a subset of ML using neural networks—turbocharged progress. Innovations like AlexNet (2012) revolutionized image recognition, while natural language processing (NLP) models began understanding human language with uncanny accuracy.
The Age of Autonomy: Agentic AI Emerges (2020s–Present)
Today, AI is undergoing another seismic shift. Traditional AI, even with ML, remains reactive—it responds to inputs but lacks agency. Agentic AI: systems that act autonomously, make decisions, and pursue goals in dynamic environments. This evolution mirrors the leap from calculators to co-pilots, transforming AI from a tool into a proactive partner.
What Is Agentic AI? Redefining Autonomy in Machines
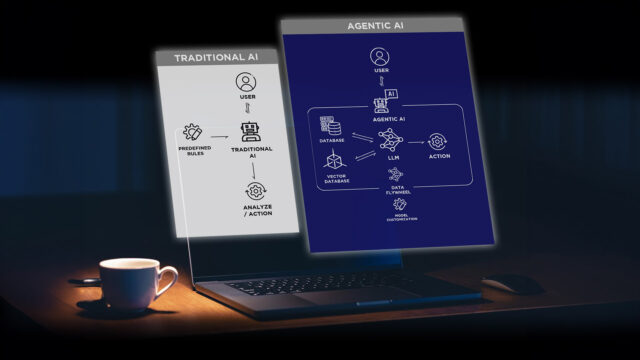
Agentic AI refers to systems that exhibit goal-driven autonomy, operating with minimal human oversight. Unlike traditional AI, which executes predefined tasks, Agentic AI can:
- Perceive its environment (via sensors, data streams, or user inputs).
- Reason using contextual understanding and probabilistic logic.
- Plan multi-step actions to achieve objectives.
- Act independently, adapting to unforeseen challenges.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
- Self-Directed Decision-Making:
Agentic AI evaluates options and chooses actions aligned with its goals. For example, an AI supply chain manager might reroute shipments during a port strike without human input. - Continuous Learning:
These systems improve over time through reinforcement learning (trial and error) or real-time data ingestion. - Multi-Agent Collaboration:
Agentic AI can coordinate with other AI agents or humans. Imagine a team of AI “employees” managing a smart factory—each specializing in logistics, quality control, or maintenance. - Ethical and Contextual Awareness:
Advanced models incorporate ethical guardrails, avoiding harmful decisions even in ambiguous scenarios.
Agentic AI vs. Traditional AI—A Head-to-Head Comparison
To grasp the revolutionary nature of Agentic AI, let’s contrast it with traditional AI:
| Feature | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
| Core Function | Executes predefined tasks (e.g., classifying images, generating reports). | Sets and pursues goals autonomously (e.g., optimizing a business strategy). |
| Learning Approach | Supervised learning (requires labeled data). | Reinforcement learning, self-supervised learning, and real-time adaptation. |
| Decision-Making | Follows fixed rules; struggles with uncertainty. | Handles ambiguity using probabilistic reasoning and contextual data. |
| Human Dependency | High (needs constant input/guidance). | Low (operates independently; humans set goals). |
| Scalability | Limited to specific tasks. | Scales across domains (e.g., an AI agent trained for customer service can adapt to HR). |
| Use Cases | Chatbots, fraud detection, predictive maintenance. | Autonomous drones, personalized education tutors, AI-driven R&D labs. |
Advantages of Agentic AI
- Solving Complex, Open-Ended Problems
Traditional AI excels at closed-loop tasks (e.g., “Identify this object”). Agentic AI tackles open-ended challenges like “Design a sustainable city” by breaking problems into sub-goals, experimenting, and iterating. - Cost and Time Efficiency
Autonomous systems reduce reliance on human labor. For instance, Boston Dynamics’ robot dogs now inspect hazardous industrial sites, eliminating risks to workers. - Hyper-Personalization
Agentic AI can tailor experiences in real time. Imagine a healthcare AI that adjusts treatment plans daily based on a patient’s vitals, diet, and genetic data. - Resilience in Dynamic Environments
From stock trading to disaster response, Agentic AI thrives in unpredictable settings. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI systems like BlueDot autonomously tracked outbreaks and predicted hotspots faster than human epidemiologists.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Agentic AI
1. Autonomous Customer Support (E-commerce & SaaS)
Instead of relying on scripted chatbot responses, Agentic AI-powered virtual assistants can resolve complex customer inquiries, process orders, offer personalized suggestions, and even escalate cases when necessary.
2. Self-Managing Financial Advisors
In fintech, AI-driven investment platforms can analyze market trends and autonomously adjust investment portfolios, ensuring optimal financial growth.
3. Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Manufacturing plants use Agentic AI to predict equipment failures, adjust production schedules, and optimize resource allocation without human oversight.
4. Healthcare and Personalized Medicine
AI agents in healthcare assist doctors by monitoring patient records, identifying potential risks, and recommending treatment plans in real-time.
5. AI-Driven Research & Development
R&D teams across pharmaceuticals, engineering, and tech use Agentic AI for hypothesis testing, simulation modeling, and accelerating innovation cycles.
The Future of AI—What’s Next?
By 2030, Agentic AI could:
- Revolutionize Education: AI tutors will adapt to each student’s learning style, pace, and interests.
- Democratize Healthcare: Low-cost AI doctors will provide diagnoses in underserved regions.
- Combat Climate Change: Autonomous systems will optimize carbon capture, renewable energy grids, and reforestation.
However, the line between “assistant” and “autonomous entity” will blur. As AI ethicist Joanna Bryson warns: “The question isn’t whether machines can think—it’s whether we’ll retain control over how they think.”
Ready to Embrace Agentic AI? Let Walden Global Services Guide You
The AI landscape is evolving faster than ever. Whether you’re exploring Agentic AI for your business or seeking to upgrade legacy systems, Walden Global Services is your trusted partner.
We offer:
- Free AI Strategy Consultation: Identify use cases aligned with your goals.
- Implementation Support: From pilot projects to full-scale deployment.
- Ethical AI Audits: Ensure your systems are fair, transparent, and compliant.
Don’t get left behind in the AI revolution. Contact us today at or visit our website to schedule your free consultation.